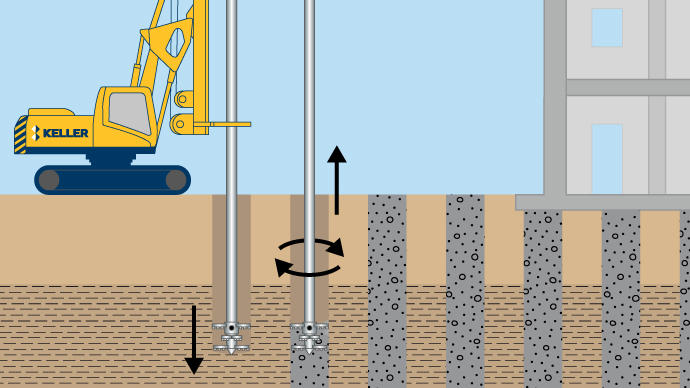
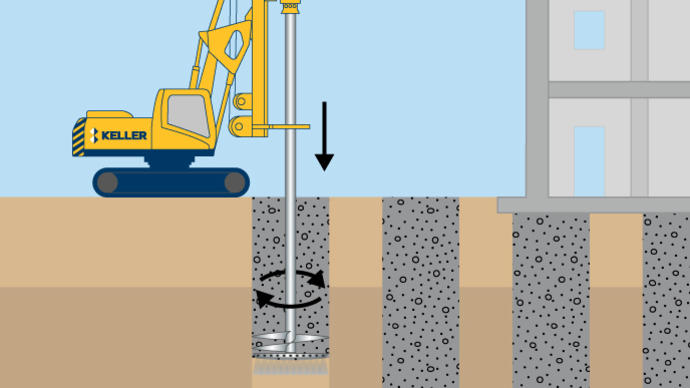
Mass soil mixing (MSM), mass mixing, or mass stabilization, is a ground improvement technique that improves soft or loose soils, by mechanically mixing them with either wet grout or dry cementitious binder.
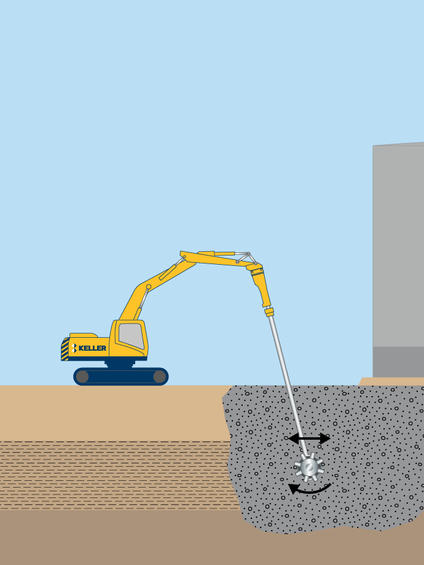
Common uses
Process
The mass soil mixing process is typically constructed in pre-defined ‘cells’ of the order of 4m x 4m in plan area. The cells are mixed adjacent to others to form a 100% mass stabilized zone, all with a designed strength and stiffness. Soils vary widely in their ability to be mixed, depending on the soil type, strength, water content, plasticity, stratigraphy, and texture. Organic soil and peats can often be stabilized, but laboratory testing is always recommended before design. Treatment is possible to depths up to 5m to 6m.
Large obstructions are pre-excavated and removed ahead of the soil mixing process. Pre-production laboratory testing determines the mix methodology, energy, and binder content. Keller has developed proprietary equipment and software for the real-time control and monitoring of mixing parameters during the mixing process. Samples are taken during production and cured in a controlled environment for testing.
Advantages
Quality assurance
Quality is controlled and assured through column installation protocols and relevant laboratory and field-verification test results. Each column is provided with a chart log, which typically comprises element identification, mixing tool details, mixing depth, mixing time, slurry specification, injection flow rate and pressure, the total volume of slurry used, mixing tool velocities, and rpm during penetration and withdrawal, and torque of the shaft.
The mixing energy and binder content are calculated from this information to match design requirements.
Specimens of stabilized soils for testing are usually obtained from fresh columns with a wet grab.
Advanced core drilling and other field-testing methods can also be used to obtain specimens and inspect the continuity, uniformity, and stiffness of deep soil mixing columns. The selection of suitable verification methods depends on their relevance, accuracy, and applicability in relation to the purpose and pattern of soil treatment and the design properties of stabilized soil.